Facebook & Google Ads Platform Are Both Good but Which One is Better?
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Should You Run Google Ads or Facebook PPC?
For most digital marketers and businesses who market online, the two most popular advertising platforms on the Internet, Google Ads & Facebook Ads, have long been regarded as fierce rivals. Advertisers the world over have often battled over which one is better for attracting visitors, garnering leads, and converting customers.
The truth is that both platforms are excellent vehicles for achieving the marketing goals stated above – if that were not so then why would both companies be making so much money in advertising revenue?
Which one will be more effective for you all depends on your aims, your niche, and your marketing strategies.
As it is impossible to know the exact marketing criteria for every reader who peruses this article, we shall compare the two by discussing each one’s features and letting the reader decide which one is best.
Let’s get started…
Paid Search vs. Paid Social
Before we list out each feature, let’s first take a look at the basic difference between the two advertising giants in the way of targeting audiences.
Google Adwords
Google Ads uses a paid search platform to allow their advertisers to bid on keywords that potential customers are typing or voice recording into the Google search engine bar.

Each time an advertiser’s ad is clicked, they must pay for that click – that is why it is called Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising.
Facebook Ads
Facebook Ads uses paid social to help potential leads and customers find the advertiser. While the advertising platform does not use keywords to target a specific audience, it does allow advertisers to show their ads to users who exhibit certain behaviors in-line with the advertiser’s criteria.

In essence, both are the same in that they offer their collected data to advertisers to find and promote to a specific audience but Google Adwords uses keywords to reach this objective and Facebook Ads uses user behavior instead .
PPC Bidding on The Different Ad Networks
Both Google Adwords and Facebook Ads use a bidding system in their auctions.
Facebook Bidding: The advertiser tells Facebook how much they want to pay (bid) for every action taken when their ad is seen
(i.e. engagement, click, like, share, etc…)
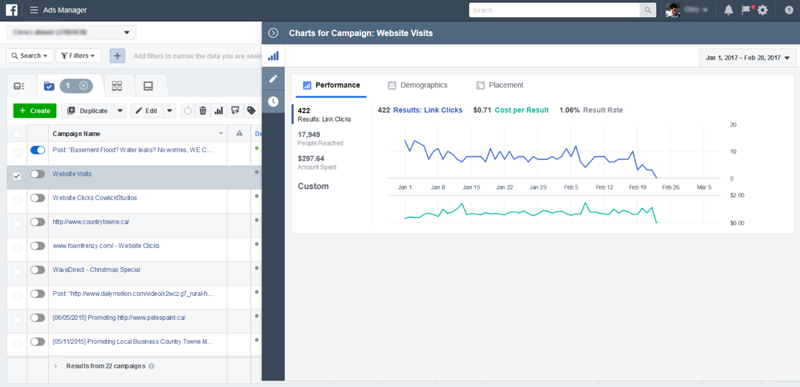
Facebook allows the following options for their bidding platform:
Choosing Goals (Objectives)
- Define Audience
- Manage Budget
- Ad Delivery Optimization
- Set Bid Amount
- Schedule Ad
- Choose Delivery Type
The bidding options are as follows:
- Auto Bidding (Facebook Chooses Bid)
- Manual Bidding (Advertiser Chooses Bid Through A Max Cap or Specific Cost For Each Action Taken)
Google Bidding: Google Adwords also allows advertisers to choose how much they bid but on a specific keyword and not on a specific action.
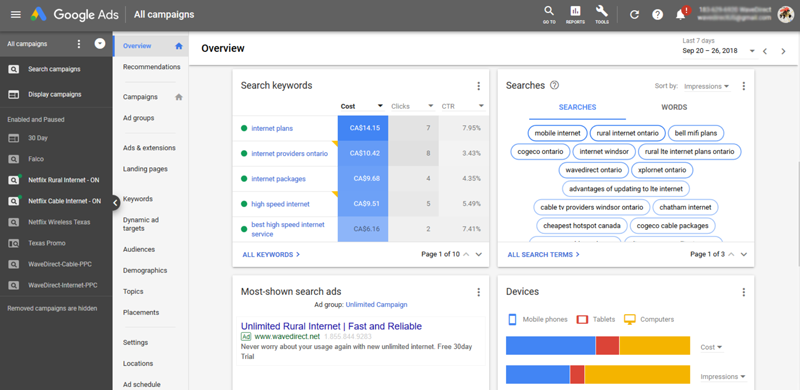
The advertiser selects a keyword or group of keywords to bid on and then Google deciphers how much they will charge the advertiser based on the following criteria:
Maximum Bid Amount (Max Price Advertiser is Willing to Pay for a Specific Keyword)
Quality Score (How Relevant the Ad is to the Keyword + How Many Times the Ad is Clicked Each Time it is Shown)
Both of the above metrics are combined to come up with what Google calls an “Ad Rank”, which ultimately determines how much they will charge for showing the advertiser’s ad(s).
Google Adwords allows the following bid options:
Manual Bidding (Advertiser Chooses Their Price)
Auto Bidding (Google Chooses Bid Price According to a Select Group of Criteria – Attempts to Maximize Clicks & Conversions by Altering the Bid Price on Regular Intervals)
Relevancy & Quality
This topic was briefly touched upon above, however, it can not be overstated enough that both companies use this metric to both qualify an ad and determine how much the advertiser should pay for it.
If a particular ad is receiving a high relevance – quality score, then both Facebook and Google will reduce the cost-per-action (CPA – Facebook) or the Cost-Per-Click (CPC – Google) and show the ad more frequently.
Facebook Ads Relevance Score: This is Facebook’s measure of how they view an ad. In other words, how beneficial and pertinent they believe it is to their users.
Facebook will increase costs and decrease the amount of time the ad is shown if they decide that an advertiser’s ad is not useful enough and vice versa if they feel the ad is highly-relevant.
Each Facebook Ad is scored from 1-10, 1 being the lowest score and 10 being the highest.
The following components are what Facebook uses to determine an ad’s relevancy score:
- Audience Definition
- Ad Freshness
- Campaign Objective
- Expected Feedback
These components are not as defined as Google’s quality score metrics are (shown below), which makes their scoring extremely subjective. This makes it harder to gauge what should be done to improve an ad should it get a low relevance score.
Google Adwords Quality Score: This is used to rate an advertiser’s chosen keyword(s) and ad(s). Google’s quality score determines the actual amount they will allow an advertiser to pay at auction for a specific keyword.
The score is multiplied by the max cost an advertiser is willing to pay for a keyword set to reach a final CPC price.
Google uses the following factors to come up with a quality score:
Click-Through-Rate (CTR – How Many Times an Ad is Clicked as Compared to How Many Times it is Shown)
- Ad Quality (Relevance to Keyword
- Quality of Landing Page (Relevance to Keyword)
- Ad Text (Relevance to Keyword)
- Historical Performance (Advertiser’s Adword Account)
Like Facebook, Google also uses a scoring scale of 1-10 to determine quality, 1 being the lowest and 10 being the highest.
Estimated Action rate
While Google takes only 2 factors into account when ranking an ad, Facebook takes 3, which increases the ability for direct response advertisements to covert.
Facebook Estimated Action Rate: Facebook is able to help marketers better choose their objective before launching their campaigns with their proprietary estimated action rate algorithm. This algorithm uses previous data to make an educated guess of what an advertiser’s results should be if they chose a particular objective.
This helps the advertiser in choosing a successful objective before they even start the campaign.
As part of this feature, Facebook will stop running a campaign if it is not able to optimize it, saving the advertiser money in the process.
Google Conversion Goals: Google Adwords does not predict any such results as Facebook does before an ad is launched but does give the advertiser the ability track each and every click and conversion through a pixel.
After collecting a bit of data, an advertiser can set their bids to “auto” in order to better optimize their conversion goals.
Basically, an advertiser has to set their objectives on their own and can only change them once they have collected some data. Of course, they might lose some money in the process before they are able to collect enough pertinent data to optimize their campaign.
Infographic to Help You Better Understand the Ad Platforms
Conclusion
In the end, Google Adwords and Facebook Ads offer two distinct and varied ways in which to target an audience and convert that audience. Which of these two platforms are best for advertisers depends on the each advertiser’s particular objective, and most importantly, where their model customers “hang out” online – Google Search, Facebook, or both.
In general, experienced marketers can perform well on both Google Adwords and Facebook Ads, while beginners are more likely to succeed on only Facebook as their ad platform has the ability to auto-optimize a campaign on an advertiser’s behalf.
Hope that helped!
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_empty_space height=”12px”][stm_partner style=”style_2″ title=”Ted Chong” logo=”2519″ position=”Ted run Ice Cube Marketing” img_size=”medium” description=”Ice Cube Marketing is a digital agency in Singapore that helps local small businesses acquire leads from PPC channels such as Facebook and Google.” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Ficecube.asia%2F|title:Ice%20Cube%20Marketing|target:%20_blank”]
How to Create Shocking SEO Plans for Electricians
The best SEO plans are the ones that work.
Learn tips and tricks here to expand your reach and attract more paying customers to your electrician website. SEOBANK offers Web Design, SEM, SEO Plans and Full seo marketing packages for electricians that are looking to generate sales leads. Contact us for an SEO strategy example that is proven to work.
Are you creating new SEO plans?
In today’s digital age, the key to any successful SEO strategy is the same: satisfy Google. It’s been the uncontested search engine leader since its inception on September 4th, 1998.
Google now boasts over 90% of search engine market shares worldwide. Why is that important and what does it mean?
Instead of trying to please dozens of search engines, you need only please one, making your SEO strategy simple and straightforward. Follow a few uncomplicated steps, and voila… your page ranking skyrockets overnight!
Whether you’re an electrician trying to drum up business on your website or a Fortune 500 company redesigning your digital presence, the SEO principles are the same.
Read on if you’re ready to learn those principles!
What is SEO?
Let’s make sure we’re speaking the same language before we jump into the meat of this article. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of adjusting your website to make it easily accessible to search engines.
Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and other popular search engines send out web crawlers to scour the web. These crawlers search through each page of your website and take snapshots of what they find. This information is sent back to their company servers where it’s dissected and stored.
When you type a query into a search engine, it quickly flips through the billions of website snapshots they’ve stored. The search engine returns these results, ranking each web page according to how well it matched the query.
SEO is all about adjusting your website so web crawlers can easily read the information. That’s the heart of SEO. Internet gurus sometimes throw a few additional elements into the mix. We’ll discuss those as well in the sections below.
SEO Essentials
How does Google determine whether your webpage matches a query? Only a handful of people actually know because Google’s constantly evolving algorithm is a closely-held, trade secret.
Fortunately, Google has taken pity on web developers. It may not publish the algorithm, but it drops hints. In 2018, we know the following components significantly impacted algorithms:
- Structured data
- Keywords
- Headers
- Content
- Dwell time
- Meta Description
- Alt Tags
- Links
The following sections will expand on these.
Structured Data
A way for search engines to make sense of the content on your website is through structured data, most notably, through the use of two tools: sitemaps and schema.
HTML sitemaps, are primarily for users so we won’t expand on them here but XML sitemaps used to organize your information so those pesky web crawlers can better understand the relationship between pages on your website.
Schema is a tool to use after you’ve built your XML sitemap. Imagine each piece in your sitemap is a wall which defines your structure. Your schema is the paint job and decoration that goes on those walls, giving your building personality.
Keywords
When a user types a query into a search engine, the engine tries to match each word to suitable web pages. One of the methods they use is to match-up the word in the query with the words on the page.
Good marketers take the time to research the most popular key terms people search for in his industry and use keywords to their advantage.
For example, an electrical contractor in Vail, Colorado may find the following are the most searched for terms in his industry:
- Vail electric repair
- Best electrician qualifications
- Where to find an electrician near me
- Common electrical issues
He should then build four web pages, one for each group of terms above.
Where, and how often, he uses those keywords on the page is a constantly evolving strategy. In the ’90s and early ’00s, keyword stuffing was the primary method, where web designers would shove as many of those words as they could onto the page.
Today, strategies have changed due primarily to the advent of Artificial intelligence (AI), which becomes more intelligent each year. AI is now quite good at determining how well the content on your webpage matches a user’s query, relying less on keywords.
Does that mean the use of keywords has disappeared altogether? Hardly. They are just used with more finesse. We recommend you use one in your introduction, one in your H1 header, one in your H2 header, and one in your conclusion.
Headers
Your headlines used as section titles for your content are described as headers. When coding in HTML, a headline is abbreviated as H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, or H6. Each headline grows progressively smaller, H1 being the largest and only used once on any page.
Drop one of your keywords in your H1 header and drop it again in one of your H2 headers.
Content
As we mentioned, AIs are much better at discerning whether users will find your content useful. The best way to address this is (you guessed it) to build helpful content, including:
- Blog Articles
- Videos
- Product Pages
- Podcasts
- Infographics
Develop professional, relevant content to your audience to rank high! You’ve hit the mark if your video could land a spot on CBS! If it looks like it wouldn’t pass muster in a 5th-grade art project, it’s time to head back to the drawing board!
To learn more, take a look at how to write great quality content.
Dwell Time
This is just a fancy way of saying how long visitors hang out on your web pages during their visit. The longer they stay on a page, the longer the dwell time. and the longer the dwell time, the higher you score in Google’s algorithm. These are determined by Google analytics.
How do you increase dwell time? You build content relevant to the keywords for the page.
Meta Description
Spend time writing an accurate, enticing meta description. Search engines may not use these descriptions in their algorithms, but they do look at visitor’s dwell times. These nifty little snippets are what users read to determine whether your website is worth visiting and are found on search engine results pages below your website’s name.
Alt Tags
Search engines are getting better at understanding images, but are still inaccurate. You can help web crawlers understand your graphics by describing each with words and placing these descriptions in the alt tag of the corresponding image.
The alt tags are part of the HTML code used to build your website and can be accessed through the backend of your website portal.
Links
Web pages link to other web pages through 3 types of links.
Internal links – links direct visitors to another webpage on the same site
Outbound links – link direct visitors to pages on someone else’s website
Inbound links (also called backlinks) – link visitors from other websites to your site
The complexities of link-building are beyond the scope of this article. Read How to Build Backlinks to walk through the most essential type of links.
Turning SEO Plans into Strategy
Components like keywords and alt tags are the short-term, mechanical portion of SEO plans, but some SEO components, such as backlinks, require a long-term strategy.
Think through your entire process for each component to build an SEO strategy template. Then create an SEO project plan from this template. If you stick to it, you’ll finish most of your SEO in 1 day. The rest will take a couple of months to finish. Remember, whether it’s SEO Plans for Electricians or any other industry, the method is the same!
If you found this article helpful, take five minutes to check out our library of other great SEO articles.





